Heart Attack vs. Cardiac Arrest
People often think that heart attack is the same thing as cardiac arrest. However, it is not true. In order to understand the difference between the heart attack and the cardiac arrest it is necessary we understand what happens in both the processes.
What is a heart attack?
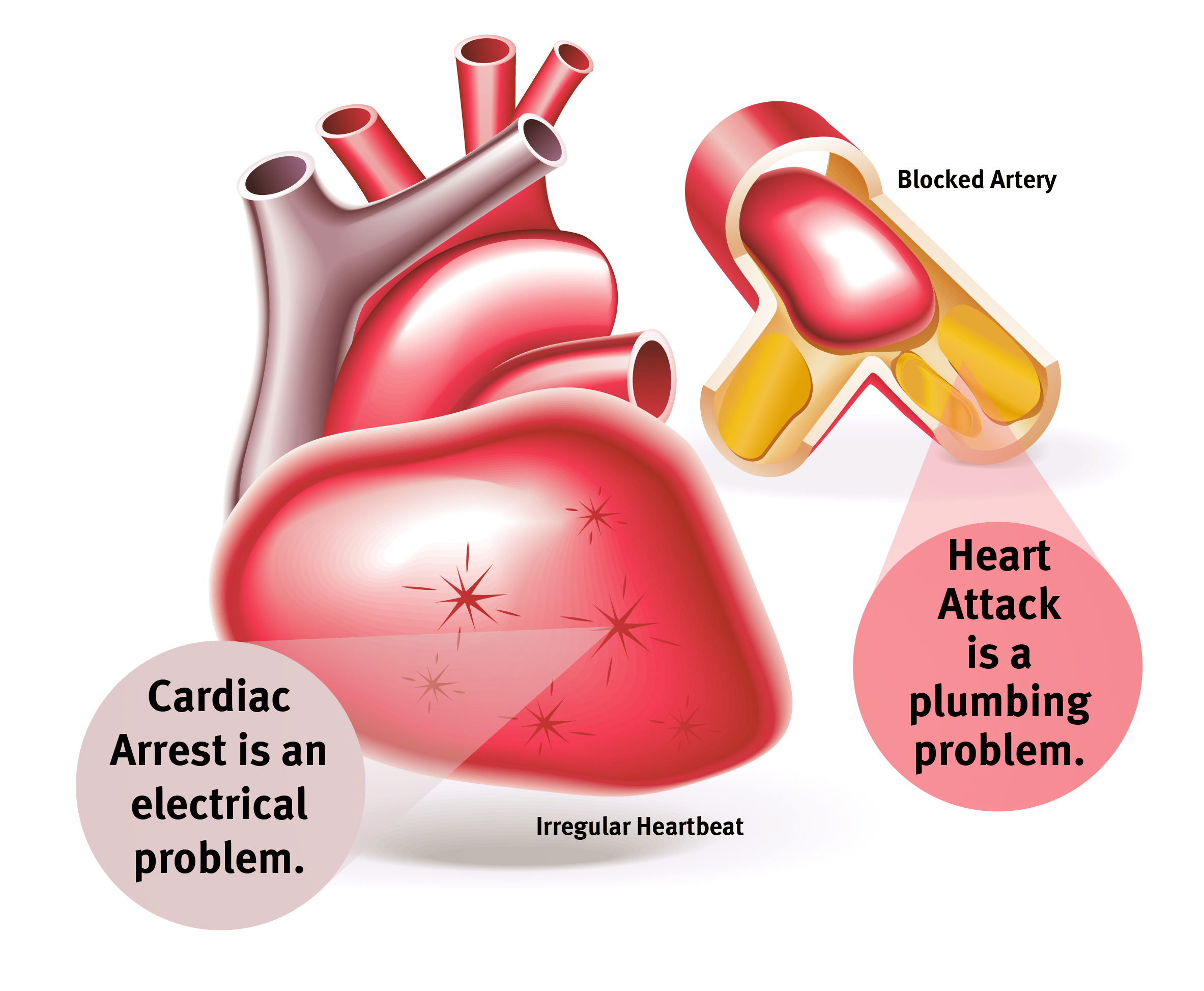
The heart is actually a type of muscles which require oxygenated blood supply continuously. This is provided to the heart by the artery known as a coronary artery. A heart attack happens when there is a blockage of the coronary arteries. The most common cause of the blockage is the blood clot. If such blockage is not quickly resolved it can cause parts of the heart muscle to begin to die.
What is a cardiac arrest?
In cardiac arrest, the heart actually stops beating whereas in heart attack normally the heart continues to beat even though the blood supply to the heart is interrupted.
Symptoms of a heart attack include
- Chest pain
- Spreading of the chest pain on other areas mostly in arms, jaws, neck, back an abdomen
- Shortness of breath
- coughing
- Wheezing
- The feeling of being sick
- Anxiety
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Sweating
- Noticeable heartbeat
Symptoms of cardiac arrest
- Sudden loss of consciousness
- Patients not responding
- No breathing
- No pulse
The lack of pulse is also caused by the heart actually stopping during the cardiac arrest. As a consequence of this, the organ of the body is deprived of blood which can also lead to the death of the patient.
Causes of heart attack
A heart attack occurs when one or more of your coronary arteries become blocked. Over the period of time, a coronary artery narrows from the building of various substances like cholesterol. During the heart attack, one of these plaques can rupture and lets other substance in the bloodstream. At the site of rupture, the clot is formed. Sometimes this clot blocks the flow of blood through the coronary artery.
Another cause is a spasm of the coronary artery that shuts blood flow to the heart muscles. A heart attack can also occur by the tear in the heart artery.
Causes of cardiac arrest
- Ventricular fibrillation or abnormal heart rhythm
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Coronary heart disease
- Change of heart structure
- Pacemaker failure
- Respiratory arrest
- Choking
- Drowning
- Electrocution
- Hypothermia
- Drop in blood pressure
- Excessive alcohol consumption